Dyness Knowledge | Anti-backflow
-
Technical Blog
-
2025-10-29
-
Dyness

Hello! Curious about a crucial concept in energy storage systems—"backflow prevention"? Don't worry, we'll explain it in the most accessible way possible. Photovoltaic Energy Storage "Backflow Prevention": Key to Ensuring Safety and Profitability. In photovoltaic and energy storage projects, "backflow prevention" is a core technical concept crucial to grid security and project profitability. Understanding it is fundamental to project success.

What is “anti-backflow”?
Imagine your factory's power supply system as a network of water pipes: The grid is like a main inlet pipe, with a constant flow of electricity (water) from the grid to the factory (forward power). The energy storage system is like the "self-contained water reservoir and pump" you install within the factory. When the self-contained pump delivers far more water than needed, the excess electricity flows to the grid. This reverse flow of electricity is called "backflow." Backflow prevention involves using technical measures to prevent this backflow of electricity back into the grid.
Why is it necessary to prevent backflow?
There are two main reasons for this. First, compliance with grid regulations: To ensure grid security and stability, most grid companies strictly prohibit unauthorized reverse power transmission, and violations will result in penalties. Second, protecting the business model: In solar-plus-storage projects jointly built by different investors, arbitrary reverse power flow would disrupt the expected flow of power, severely damaging the investment returns of any party.
How to prevent backflow? — From simple and crude to flexible and intelligent
Backflow prevention technology has evolved from "rigid" to "flexible": Rigid backflow prevention: Upon detecting backflow, the grid-connected switch is immediately disconnected. This method is reliable, but wastes power generation. Frequent starts and stops can cause voltage fluctuations and flicker, shortening the life of circuit breakers. Flexible backflow prevention (the current mainstream) utilizes real-time coordination through the energy management system (EMS). When power generation is predicted to exceed consumption, the EMS instructs the PV inverter to smoothly reduce power, minimizing the impact on the grid and loads, and discarding only the unavoidable small amount of energy.
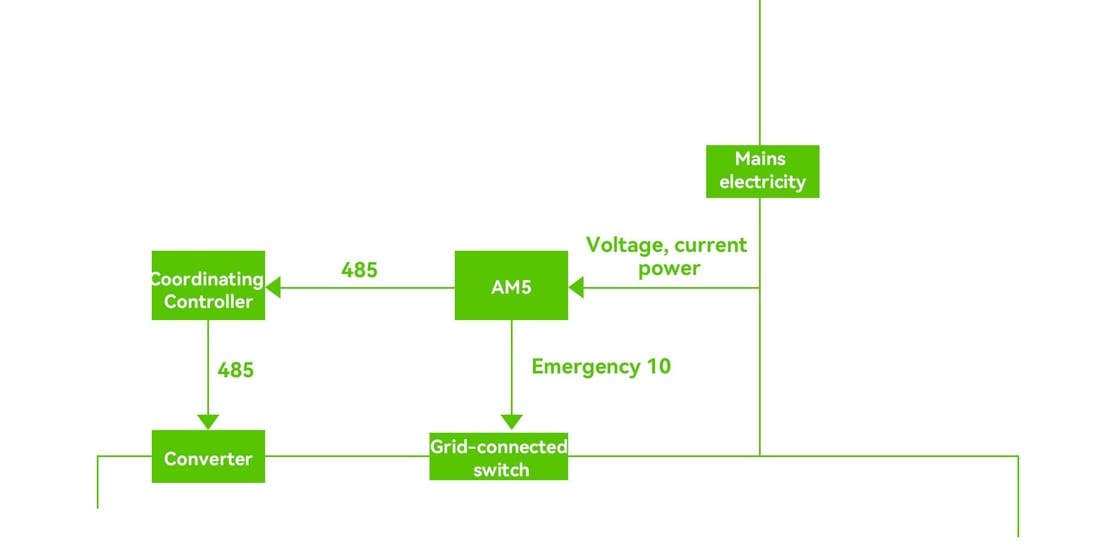
Our Advanced Strategy: Refined Model to Guarantee Profits
Our system comes standard with advanced "flexible backflow prevention" and offers two refined strategies to address complex business scenarios. General backflow prevention mode: Directly prohibits energy storage from charging from PV panels and discharging to the grid. Key backflow prevention mode (core advantage): When excess power is detected, it prioritizes charging the energy storage system, storing the excess power and increasing the revenue generated by energy storage.
Practical value: Cracking the project's "profit trap"
Project example: A factory in Jiangsu, 2MW of PV (Investor A) + 3MWh of energy storage (Investor B).
Project example: 100kW PV + 215kWh energy storage in a park in Guangdong (same investor)
When photovoltaic power and energy storage are invested by the same party, the priority of preventing backflow can be selected according to demand, and surplus photovoltaic power can be used to charge energy storage to ensure the overall profit of the power station.
Dyness Digital Energy Technology Co., LTD
WhatsApp: +86 181 3643 0896 Email: info@dyness-tech.com
Address: No.688, Liupu Road, Suzhou, Jiangsu China
Dyness Website: https://www.dyness.com/
Dyness community: https://www.facebook.com/groups/73560020090