Dyness Knowledge | EMS Communication Architecture: A Deep Dive into Master-Slave and Distributed Systems
-
Technical Blog
-
2026-01-23
-
Dyness

In energy storage and microgrids, the Energy Management System (EMS) acts as the "brain" that coordinates all devices, and its communication architecture directly determines system performance. The mainstream solutions are divided into "master-slave architecture" and "distributed architecture," which differ significantly in their core concepts.
Master-slave architecture: Centralized control
This is a centralized hierarchical model.
Architecture: A central master station acts as the sole control unit, controlling multiple slave devices (such as PCS and BMS) via a bus (such as RS485) or a star connection. The data flow strictly follows the path from slave to master to slave; there is no direct communication between slave devices.
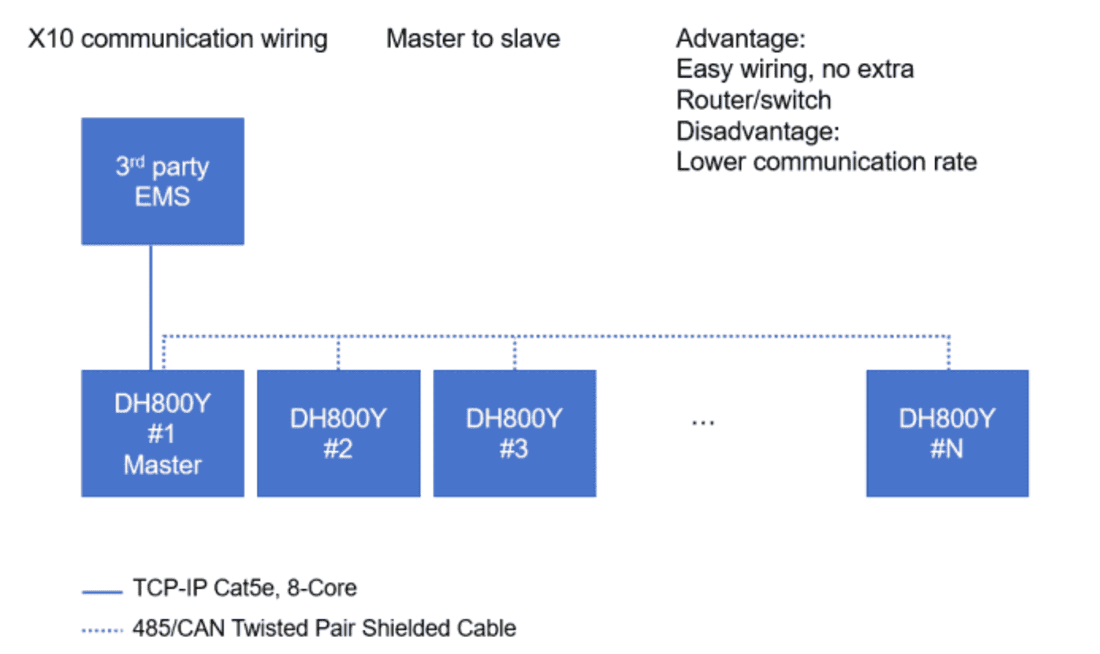
Advantages
Simple control: All logic is centralized in the master station, making it easy to develop, debug, and implement complex algorithms.
Lower cost: The master station requires high performance, while the slave stations only need basic functions, keeping hardware and wiring costs manageable.
Unified data: All data is collected at a single point, facilitating monitoring, storage, and analysis.
Disadvantages
Single point of failure: If the main station fails, the system collapses; reliability heavily depends on the redundancy of the main station.
Poor scalability: Adding or removing devices often requires modifying the main station program, and the bus has node limitations.
Bottleneck issues: All data is routed through the main station, which can easily lead to delays as the system scales up, affecting real-time control.
Discrete architecture: distributed collaboration
This is a decentralized peer-to-peer network model.
Architecture: There is no single central station in the system. Each intelligent device (such as PCS and BMS) acts as an equal network node, interconnected via industrial Ethernet (such as Ethernet TCP/IP), allowing for direct communication. The control logic is distributed across the site-level EMS.
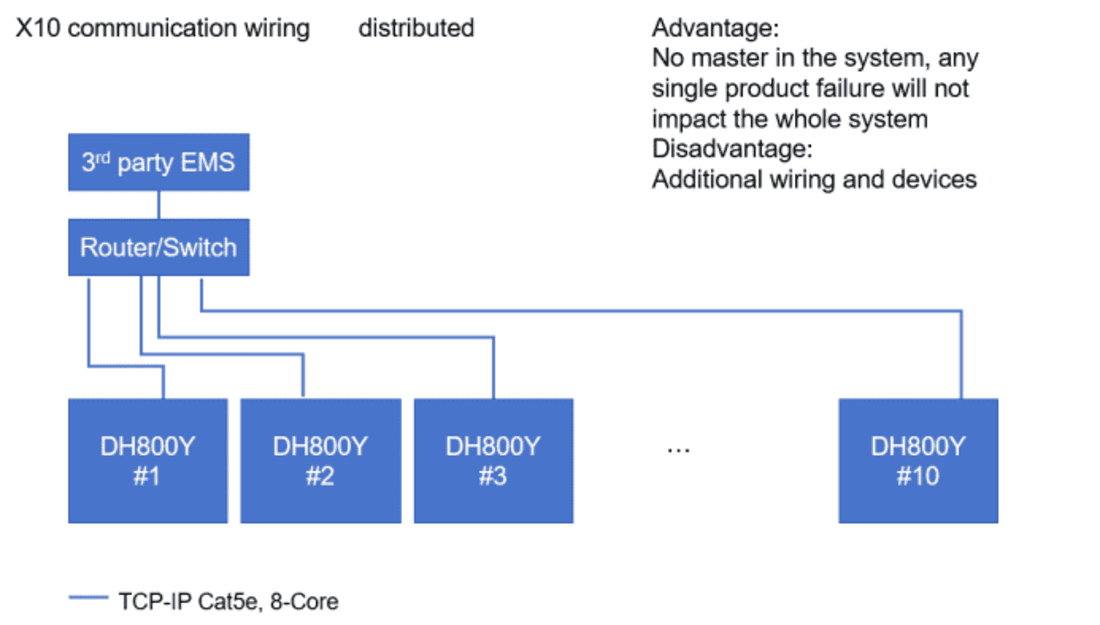
Advantages
High reliability: No single point of failure; if any node fails, the remaining devices can still operate, and the system degrades gracefully without crashing.
Strong scalability: Based on standard IP networks, adding devices is as simple as expanding a local area network, making it extremely flexible.
High real-time performance: Devices communicate directly with each other, resulting in the shortest possible path and meeting the need for millisecond-level rapid response.
Disadvantages
Complex design: Distributed logic and collaborative mechanisms are difficult to design, and integration and debugging are complex.
High initial cost: Requires devices with stronger computing power and network interfaces, resulting in higher network infrastructure costs.
Data dispersion: Requires additional systems for global data aggregation and unified monitoring.
Core Comparison and Selection
Master-slave architecture: Suitable for small and medium-sized projects with fixed patterns and cost constraints, prioritizing quick deployment and simple management.
Distributed architecture: Suitable for large, complex scenarios requiring high reliability and flexible scalability, such as large-scale energy storage power plants or multi-energy complementary parks.
Trend: Hybrid architecture
In practice, hybrid architectures have become mainstream. They combine the advantages of both approaches: "centralized optimization, distributed execution." This means using a central EMS for minute/hour-level global economic optimization, while delegating fast control and safety logic at the second/millisecond level to edge controllers or local devices. This layered design balances reliability, real-time performance, and intelligent management, representing the future direction of development.
Dyness Digital Energy Technology Co., LTD
WhatsApp: +86 181 3643 0896 Email: info@dyness-tech.com
Address:7th–8th Floors, Building 3 No. 58 Nanhu Road Chengnan Subdistrict, Wuzhong District Suzhou, China
Dyness Website: https://www.dyness.com/
Dyness community: https://www.facebook.com/groups/73560020090